Linear cell-penetrating peptides can improve and enhance the delivery of oligonucleotide drugs, but linear peptides are still unstable to proteolytic enzymes and may limit oligonucleotide delivery and efficacy and safety. Cyclization of cellular transmembrane peptides can improve their stability and improve the efficiency of oligonucleotide drug delivery.
The method of preparing cyclic peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates is mainly by liquid phase connection. That is, linear peptides are synthesized first, then the linear peptides are cyclized to form cyclic peptide fragments, and then the cyclic peptide fragments and oligonucleotide fragments are connected to form cyclic peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates through chemoselective reactions. In addition, cyclized cell-osmotic peptides often contain multiple positively charged arginine or lysine, which will aggregate or precipitate with negatively charged oligonucleotides during reaction. The solid-phase method can avoid this problem of aggregation and precipitation.
As with the preparation of linear peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates by solid-phase synthesis, the destruction of oligonucleotides by trifluoroacetic acid also needs to be considered when preparing cyclic peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates by solid-phase synthesis, so it is also necessary to avoid the use of trifluoroacetic acid. Another important issue considered in the preparation of cyclic peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates by solid-phase synthesis method is the cyclization of peptide fragments. The simplest way to cyclize polypeptides is to ring with dibrominated small molecules by sulfhydryl groups, which is a fairly mature reaction at the peptide level, but cyclic peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates include not only polypeptides, but also oligonucleotides, and it is best to cyclize with the presence of sulfhydryl groups, so it is necessary to prepare cyclic peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates containing sulfhydryl groups. The sulfhydryl protection group of hemiphotoine is generally triphenylmethyl (Trt), but triphenylmethyl (Trt) finally needs to be removed from trifluoroacetic acid, which is definitely incompatible with solid-phase synthesis systems. Therefore, a suitable cysteine sulfhydryl protection group needs to be found to prepare cyclic peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates. StBu can form a disulfide bond with cysteine to protect cysteine, and only a reducing agent can remove this protective group. There is no reducing agent involved in the synthesis of solid-phase peptides and solid-phase oligonucleotides, so in theory, StBu exists stably in these two solid-phase synthesis processes, and Fmoc-Cys(StBu)OH can be used to synthesize amino acids.
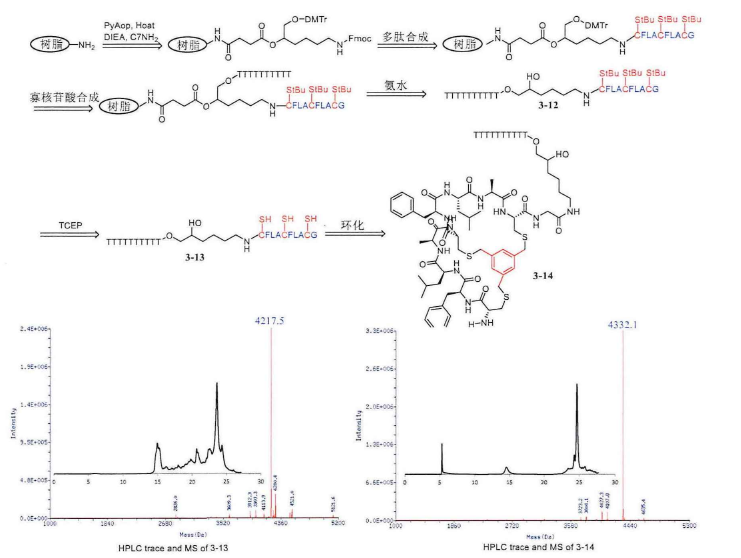
[Solid-phase condensation of cyclic peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates, liquid-phase ringing]
The operation steps of cyclic peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates before ring formation are the same as those of linear peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates, which are first carried out for peptide synthesis and then for the synthesis of solid-phase oligonucleotides. First, the resin needs to be connected to a small C7-NH2 molecule, the N-terminus of this small molecule is protected by Fmoc, where peptide synthesis can be carried out, hydroxyl group is protected by DMTr, and solid-phase oligonucleotide synthesis can be carried out here. Then, the Fmoc protective group on the small molecule was removed with 20% piperidine, and the remaining amino acids were sequentially coupled to the C7-NH2 molecule. The amino groups of tryptophan, histidine, arginine and lysine side chains need to be protected with Boc, the hydroxyl groups of serine, tyrosine, threonine side chains are protected with TBS, and the sulfhydryl groups of cysteine are protected by StBu. The end of peptide synthesis requires the drying of the solid-phase carrier and then the synthesis of solid-phase oligonucleotides. After the synthesis, the polypeptide-oligonucleotide conjugate containing cysteine is cut off from the resin directly with ammonia. At this time, according to the design of the experiment, the protective group should continue to retain on the peptide-oligonucleotide conjugate, without purification, the StBu protective group of cysteine acid can be completely removed by dissolving the reaction with TCEP solution for 1 hour, purifying and lyophilizing and 1,3-di(bromomethyl)benzene in the solution for ring formation, and monitoring the reaction process by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), generally one hour can be successfully cyclized.
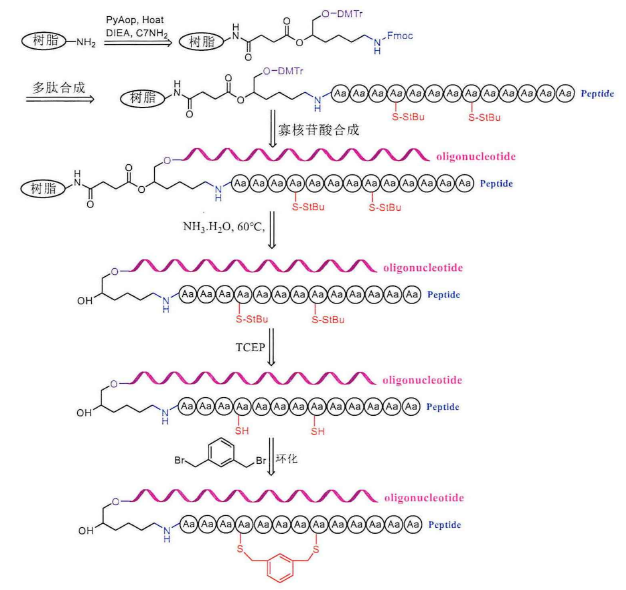
【Monacyclic peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates】
There is only one cysteine, which cannot be cyclized and generally needs to contain 2 cysteines. The synthesis steps are the same as those described above. After removing the two StBu protective groups on the peptide-oligonucleotide conjugate, cyclic peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates can be synthesized by using the principle of 1,3-dis(bromomethyl)benzene and two sulfhydryl groups in solution.
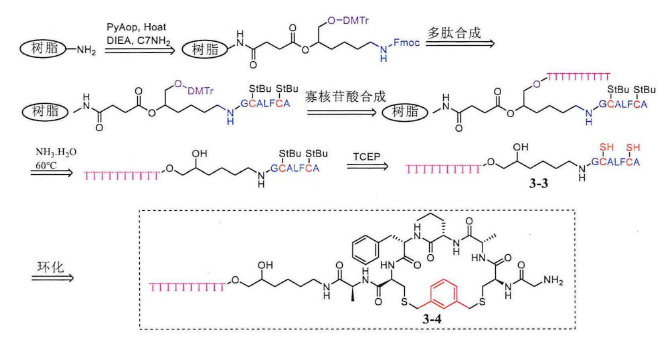
In addition to di(bromomethyl) benzene, ring-forming linkers can also be other types of linkers. Monacyclic peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates can also be synthesized from alkyl olefins and biphenyls, the difference is mainly that in the last step of ring formation, alkyl olefins and biphenyls are used to replace di(bromomethyl)benzene, and the reaction time is also 1 hour.
[Synthesis of bicyclic peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates]
In addition to monocyclic peptides, there are also bicyclic peptides, which react with two cysteines and 1,3-dis(bromomethyl)benzene to form a monocyclic structure, and if you want to form a bicyclic structure, you must have three cysteines, and then react with 1,3,5-tris(bromomethyl)benzene and three mercaptogroups to form a bicyclic peptide.
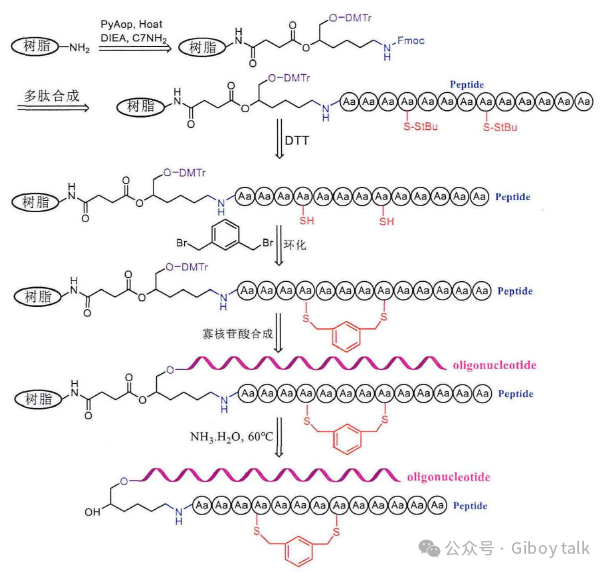
[Solid-phase condensation of cyclic peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates, solid-phase ringing]
The above-mentioned method of solid-phase coupling liquid phase ring formation is used to prepare cyclic peptides, but this method still has certain shortcomings. We need to consider the stability of cysteine in ammonia, which can produce a large number of β elimination by-products if not paid attention to. The cyclization of peptides can be directly realized on the resin, on the resin is attached to a small C7-NH2 molecule, the N-terminal of this small molecule is protected by Fmoc, where peptide synthesis can be carried out, hydroxyl group is protected by DMTr, and solid-phase oligonucleotide synthesis can be carried out here. Then use 20% piperidine to remove the Fmoc protective group on the small molecule, and conjugate the amino acids in order, and then use a reducing agent such as DTT or dimercaptoethanol on the resin to remove the StBu protective group on the peptide cysteine first, so that the sulfhydride group on the peptide will leak out. The resin is then ring-forming with 1,3-dis(bromomethyl)benzene and exposed sulfhydryl groups. If the cyclization is successful, the solvent in the resin is drained, and then the solid-phase oligonucleotides are synthesized. Then the cyclic peptide-oligonucleotide conjugate is cut off from the resin with ammonia, and at this time, because the peptide has been successfully cyclocycized, the original cysteine has now become a sulfide bond, so there is no need to worry about the damage of ammonia to it, so as to avoid the elimination side reaction of the sulfhydryl group always encountered by the previous solid-phase synthesis of cyclic peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates.
Although linear cell transmembrane peptides can improve and enhance the delivery of oligonucleotide drugs, the presence of ubiquitous proteolytic enzymes makes linear cell-penetrating peptides unstable and limits the efficacy of oligonucleotides. Cyclization of peptides can improve their stability and improve oligonucleotide drug delivery. The current method of preparing cyclic peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates is mainly by liquid phase connection. However, cyclized cell transmembrane peptides usually contain multiple positively charged arginine or lysine, which will aggregate or precipitate with negatively charged oligonucleotides when connected by liquid phase method. The solid-phase method can avoid this problem of aggregation and precipitation.